The sun is the number one cause of skin hyperpigmentation, so effective sun protection is the most important step you can take to help prevent hyperpigmentation. This article outlines the different types of hyperpigmentation and explains how to protect your skin and keep it even and radiant.
What is hyperpigmentation?
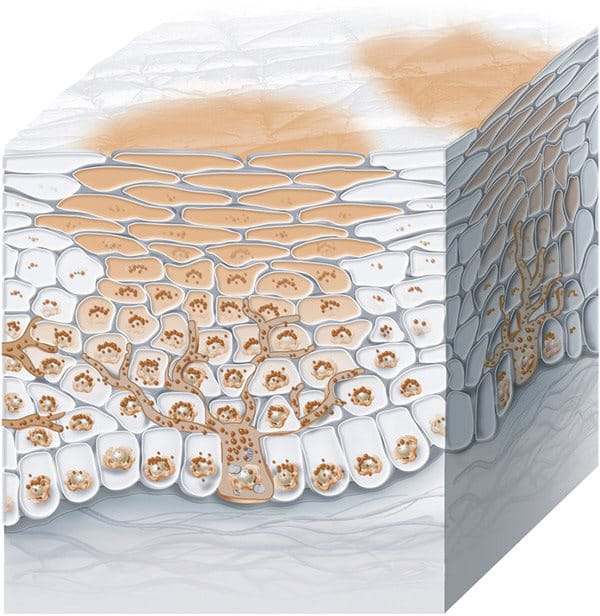
Hyperpigmentation is the word used to describe areas of uneven pigmentation in skin.
Hyperpigmentation appears as darkened patches or spots on the skin that make it look uneven. These dark spots are known as sun spots or age spots and hyperpigmentation is also at the heart of skin conditions such as post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation. Hyperpigmentation typically appears on areas of skin that are regularly exposed to the sun such as the face and hands.
What causes and/or triggers dark spots on skin?

Hyperpigmentation is caused by an increase in melanin production. Melanin is the natural pigment that gives our skin, hair and eyes their color. This increased production is triggered by a variety of factors, but the main ones are sun exposure, age, hormonal influences and skin injuries or inflammation.
Sun exposure is the number one cause of hyperpigmentation as it’s sunlight that triggers the production of melanin in the first place. Melanin acts as your skin’s natural sunscreen by protecting you from harmful rays, which is why people tan in the sun. But excessive sun exposure can disrupt this process, leading to hyperpigmentation.
Oxidative stress caused by the sun’s UVA and UVB rays are the primary cause of premature skin aging and skin hyperpigmentation issues, but recent studies have shown that high-energy visible light, the light we see all around us, also causes oxidative stress to skin and can also contribute to hyperpigmentation.1,2
1 Mahmoud BH, Ruvolo E, Hexsel CL, Liu Y, Owen MR, Kollias N, et al. Impact of long-wavelength UVA and visible light on melanocompetent skin. J Invest Dermatol. 2010;130(8):2092–2097. doi: 10.1038/jid.2010.95.
2 Duteil L, Cardot-Leccia N, Queille-Roussel C, Maubert Y, Harmelin Y, Boukari F, et al. Differences in visible light-induced pigmentation according to wavelengths: a clinical and histological study in comparison with UVB exposure. Pigment Cell Melanoma Res. 2014;27(5):822–826. doi: 10.1111/pcmr.12273.
Sun spots on skin
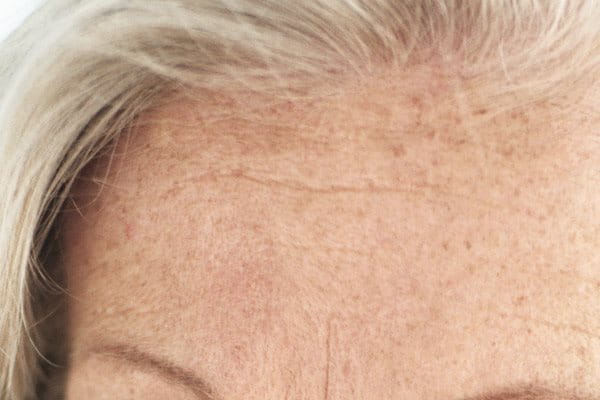

Small, darkened patches of skin known as sun spots are, as the name suggests, caused by sun exposure. They commonly appear on skin that is frequently exposed to the sun such as the face, neck, décolleté and hands. Once dark spots have developed, sun exposure can also exacerbate the issue by making then even darker.
Another common name for sun spots is age spots. As skin ages, the number of melanin-producing cells (known as melanocytes) decreases but the remaining ones increase in size and their distribution becomes more focused. These physiological changes explain the increase of age/sun spots in those over 40. You can read more in skin aging.
Melasma and the sun

Melasma, which manifests itself as larger patches of hyperpigmentation mainly on the face, is particularly common among women. It is thought to occur when the female sex hormones estrogen and progesterone stimulate the overproduction of melanin when skin is exposed to the sun. It occurs in 10–15 percent of pregnant women and in 10–25 percent of women taking oral contraceptives.3
Whilst the primary trigger is hormonal, sunlight can drive the melasma process an exacerbate the condition. You can read more about melasma in What causes melasma and how can I reduce dark patches on my skin?3.
3 The International Dermal Institute, Melasma Unmasked by Dr Clauida Aguirre quoting Kang, H. Y., & Ortonne, J. P. (2010). What should be considered in treatment of melasma. Annals of Dermatology, 22(4), 373-378.
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation and the sun
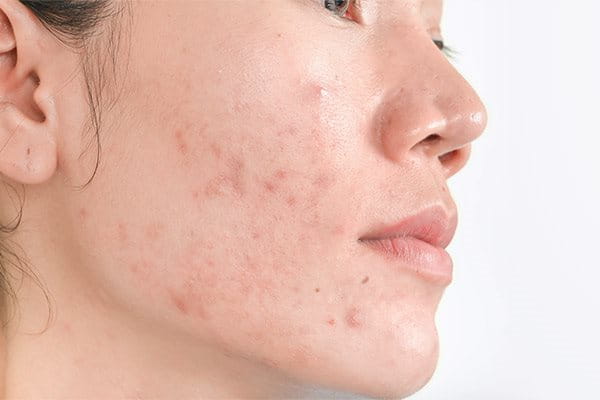
Post-inflammatory hyperpigmentation occurs when a skin injury or trauma heals and leaves a flat area of discolouration behind. It’s commonly found among acne, Atopic Dermatitis or Psoriasis patients and can also be caused by cosmetic procedures such as dermabrasion, laser treatment and chemical peels. The condition is worsened by overexposure to the sun’s UV rays4.
4 Postinflammatory hypopigmentation and hyperpigmentation. Ruiz-Maldonado R, Orozco-Covarrubias ML Semin Cutan Med Surg. 1997 Mar; 16(1):36-43.
How can I protect my skin from hyperpigmentation?

Whatever your skin’s natural color, sun protection is the most significant step you can take in helping to prevent hyperpigmentation in the first place. It’s important to remember that the sun’s rays affect skin even on cloudy days, so give your skin the daily protection it needs. Be sure to apply the product thoroughly and reapply when appropriate.
Limiting skin’s exposure to the sun will also help to reduce instances of hyperpigmentation. Try to keep out of the sun during its most intense hours and wear protective clothing including sunhats and glasses whenever possible.
If you are already concerned by hyperpigmentation in your skin then a sensible attitude to sun exposure and sun protection will help you to prevent the condition from worsening.
What should I look for in a sun protection product?
Look for products that offer high or very high protection from UVA and UVB rays – that means products that are clearly marked with a UVB protection of at least SPF 30 plus reputable UVA filters. We also recommend that you choose products that offer high-energy visible light defence and that are tailored to your skin type and condition
Eucerin Sun Fluid Pigment Control SPF 50+ has been specially formulated to help prevent sun-induced hyperpigmentation. The Advanced Spectral Technology combines broadband and photostable UVA/UVB filters1 for very high UV protection with Licochalcone A to neutralize free radicals caused by UV and HEVIS light. The formula also includes Glycyrrhetinic Acid which supports skin’s own DNA repair mechanism and the unique and patented active Thiamidol that acts at the root cause of hyperpigmentation.While prevention is best, once you have pigment spots Thiamidol is clinically and dermatologically proven to reduce dark spots and prevent their re-appearance. Eucerin Sun Fluid Pigment Control SPF 50+ can be used alongside other products in the Eucerin Anti-Pigment range to help reduce pigment spots.5.
5 Use a maximum of four application of products containing Thiamidol per day
Our brand values

We deliver a holistic dermo-cosmetic approach to protect your skin, keep it healthy and radiant.

We work together with leading dermatologist and pharmacist partners around the world to create innovative and effective skincare products they can trust and recommend.

For over 100 years, we have dedicated ourselves to researching and innovating in the field of skin science. We believe in creating active ingredients and soothing formulas with high tolerability that work to help you live your life better each day.











